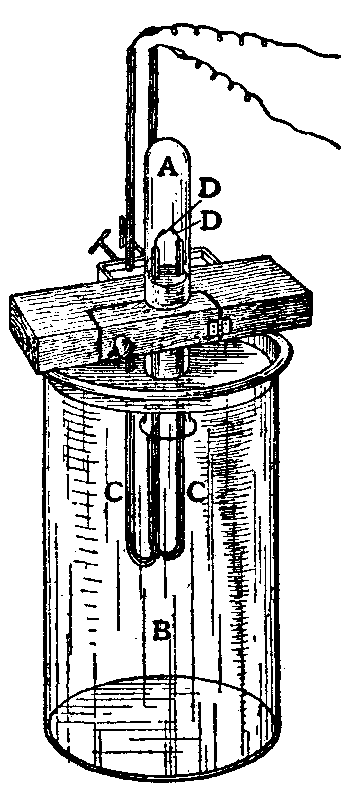
Argon was first isolated from the air in 1894 by Lord Rayleigh and Sir William Ramsay of University College London, removing oxygen, carbon dioxide, water and nitrogen from a sample of clean air. They captured a mixture of atmospheric air with extra oxygen in a tube (A) upside down over a large amount of dilute alkaline solution (B), which in Cavendish's original experiment was potassium hydroxide, and passed the current through wires insulated by U-shaped glass tubes (CC), which sealed the platinum wire electrodes, leaving the ends of the wires (DD) exposed to the gas and isolated from the alkaline solution. . The arc was powered by a battery consisting of five Grove cells and a medium-sized Ruhmkorff coil. Alkalis absorb the nitrogen oxides produced by the arc, as well as carbon dioxide. They worked on the arc until no further reduction of the gas volume was seen for at least an hour or two, and the spectral lines of nitrogen disappeared during the study of the gas. The remaining oxygen was reacted with alkaline pyrogallan, leaving a seemingly non-reactive gas, which they called argon.