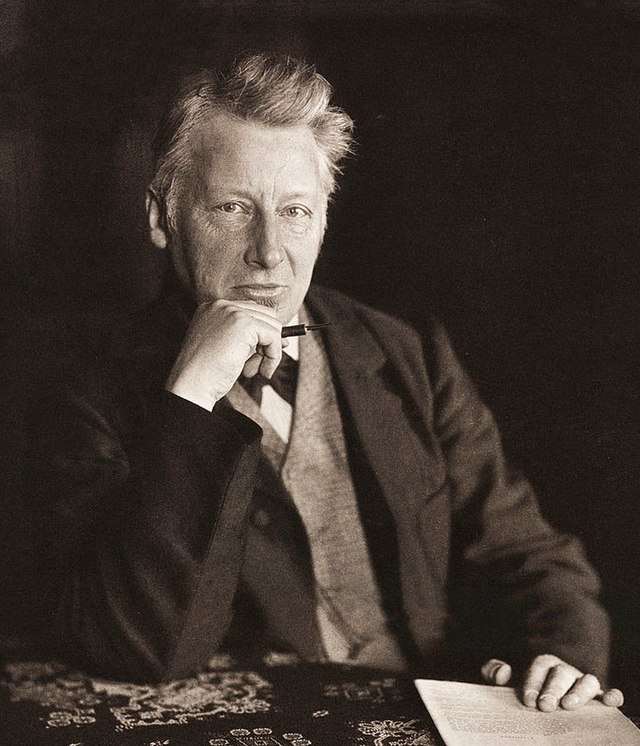
He was the first recipient of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. His pioneering work contributed to the discovery of contemporary theories of chemical affinity, chemical equilibrium, chemical kinetics, and chemical thermodynamics. Van't Hoff formulated the theory of carbon tetrahedrons in his 1874 pamphlet, laying the foundations for stereochemistry, describing the phenomenon of optical activity, assuming that the chemical bonds between carbon atoms and their neighbors are directed towards the corners of a regular tetrahedron. He shares the credit of the French chemist Joseph Le Bel, who independently came up with the same idea. In 1875, he predicted the correct structures of allen and cumulene and their axial chirality. He is also widely regarded as one of the creators of physical chemistry.